Designing a Scalable Event Booking System with AI-Powered Precision
Building a robust online ticket booking system requires more than just visual clarity—it demands architectural intelligence. The challenge lies in modeling complex interactions between user-facing components, business logic, and external services while maintaining clean separation of concerns. Enter the Visual Paradigm AI Chatbot: not just a diagram generator, but a conversational design partner that transforms abstract ideas into precise, standards-compliant models through natural language.
From Idea to Architecture: A Collaborative Modeling Journey
The journey began with a simple prompt: “Produce a component diagram to represent an online ticket booking system showing user interface, event catalog, seat selection, payment service, and confirmation service.” Within seconds, the AI Chatbot delivered a fully structured PlantUML code snippet, automatically organizing components into layered architecture—Presentation, Application, and Service layers—using best practices in UML component modeling.
But the real value emerged in the conversation. When asked, “Can you explain how the ‘Fetch Event Catalog’ interface interacts with the underlying database?”, the AI didn’t just restate the diagram—it provided a deep technical explanation of the data access flow, including:
- How the Event Catalog component acts as an intermediary between the UI and the database
- What happens behind the scenes when a user requests event listings
- Why a data access layer (DAL) or repository pattern is essential for maintainability
- Even included a sample SQL query to illustrate real-world implementation
This wasn’t a static diagram. It was a living design conversation—where each follow-up request refined the model’s logic, clarity, and architectural fidelity. The AI didn’t just generate; it explained, advised, and evolved the design in real time.
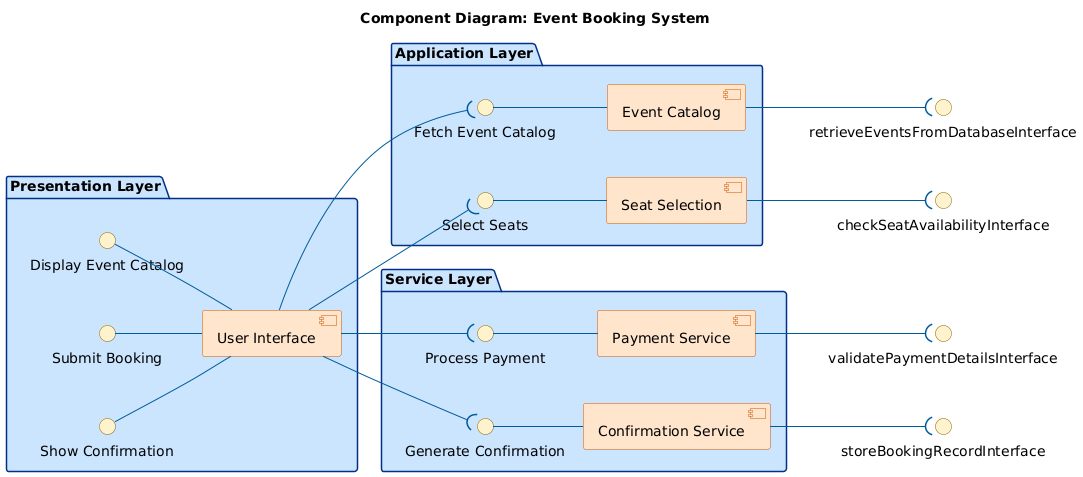
Decoding the Component Diagram Logic
The resulting diagram reflects a modern, layered architecture designed for scalability and maintainability. Here’s how each element contributes:
1. Layered Component Structure
- Presentation Layer: Houses the User Interface and defines the interfaces it exposes—Display Event Catalog, Submit Booking, and Show Confirmation.
- Application Layer: Contains the core business logic—Event Catalog and Seat Selection—each with their own internal interfaces for data retrieval and user interaction.
- Service Layer: Encapsulates externalized functionality—Payment Service and Confirmation Service—that are called by the UI to complete the booking workflow.
2. Interface-Based Communication
Each component communicates through well-defined interfaces. For example:
- The User Interface requires the Fetch Event Catalog interface to load event data.
- The Seat Selection component depends on Select Seats to validate availability.
- The Payment Service implements Process Payment to handle transaction logic.
This interface-first design ensures loose coupling—components can be modified or replaced without breaking the entire system.
3. Why Component Diagrams?
Component diagrams are ideal for this use case because they:
- Visualize system modularity
- Clarify responsibility boundaries
- Support scalability and team collaboration
- Align with DevOps and microservices practices
By modeling the system as a collection of replaceable, composable components, the design supports agile development, independent deployment, and long-term maintainability.
Conversational Intelligence in Action
The true strength of the Visual Paradigm AI Chatbot lies in its ability to function as a modeling consultant. The conversation didn’t end at diagram generation—it deepened with each question. When the user asked for clarification on database interaction, the AI didn’t default to a generic answer. Instead, it:
- Explained the role of the data access layer
- Highlighted architectural best practices
- Provided concrete implementation examples (e.g., SQL query)
- Offered a path forward: “Let me know if you’d like a version of the diagram that includes a database component or data access layer explicitly!”
This level of contextual understanding transforms the tool from a diagramming utility into a strategic design collaborator.
More Than Just Component Diagrams: A Full-Stack Modeling Platform
While this example focused on a Component Diagram, the Visual Paradigm AI Chatbot is not limited to one standard. It supports a full suite of modeling languages, including:
- UML: For detailed system and software design
- ArchiMate: For enterprise architecture and business capability modeling
- SysML: For systems engineering and complex system design
- C4 Model: For software architecture visualization at multiple abstraction levels
- Mind Maps, Org Charts, SWOT, PEST, and Charts: For strategic planning and business analysis
Whether you’re designing a microservices backend, mapping business capabilities, or visualizing team structure, the AI Chatbot adapts to your needs—delivering accurate, standards-compliant diagrams in natural language.
Conclusion: Build Smarter, Faster, Together
Designing a scalable event booking system isn’t just about drawing boxes and lines. It’s about modeling intelligent, maintainable systems with clear boundaries, well-defined interactions, and future-proof architecture. The Visual Paradigm AI Chatbot turns this challenge into a collaborative dialogue—where every question leads to deeper insight, and every iteration strengthens the design.
Ready to bring your next system to life? Try the AI Chatbot today and experience the future of visual modeling.
Related Links
- Component Diagram – Wikipedia: A UML diagram that illustrates the organization and dependencies of components in a software system.
- What is a Component Diagram? – Visual Paradigm: A detailed guide on UML component diagrams, showing how components interact and are structured in software design.
- Component Diagram Tutorial: Component Diagram Tutorial. Component diagrams provide a simplified, high-order view of a large system. Classifying groups of classes into components supports the interchangeability…


