Chart
Charts transform your data into clear visual insights, making complex information easy to understand and present effectively.
Instant Chart Creation
With the AI chatbot, you can turn raw data into a polished chart instantly. Instead of adjusting settings or formatting manually, you simply describe what you want to visualize. The chatbot interprets your intent, identifies the best chart type, and produces a clear, structured visualization in seconds. Whether you provide a short text description or a small dataset, the AI transforms it into a meaningful chart without any extra steps.
Refine Your Visualization Through Conversation
Once your chart is generated, enhancing it is as simple as asking. You can adjust labels, switch chart types, add new data points, or highlight specific trends through natural conversation. Want to compare another year? Change the scale? Add annotations? Just ask, and the chatbot updates the chart for you. This conversational workflow makes chart creation flexible, interactive, and much easier than traditional manual editing.

Benefits of Creating Charts with the AI Chatbot
Create charts instantly from plain text, tables, or short descriptions
Get automatic recommendations for the most appropriate chart type
Update or expand your chart through simple follow-up prompts
Generate presentation-ready visuals without manual formatting
Easily explore different perspectives by switching chart types on demand
Save time when preparing reports, dashboards, or visual summaries
Improve clarity and insight by letting AI interpret and organize your data
Examples of Generating Chart
Use simple text prompts to generate this diagram in seconds. Here are a few examples to get you started:
Budget by Department (Bar Chart)
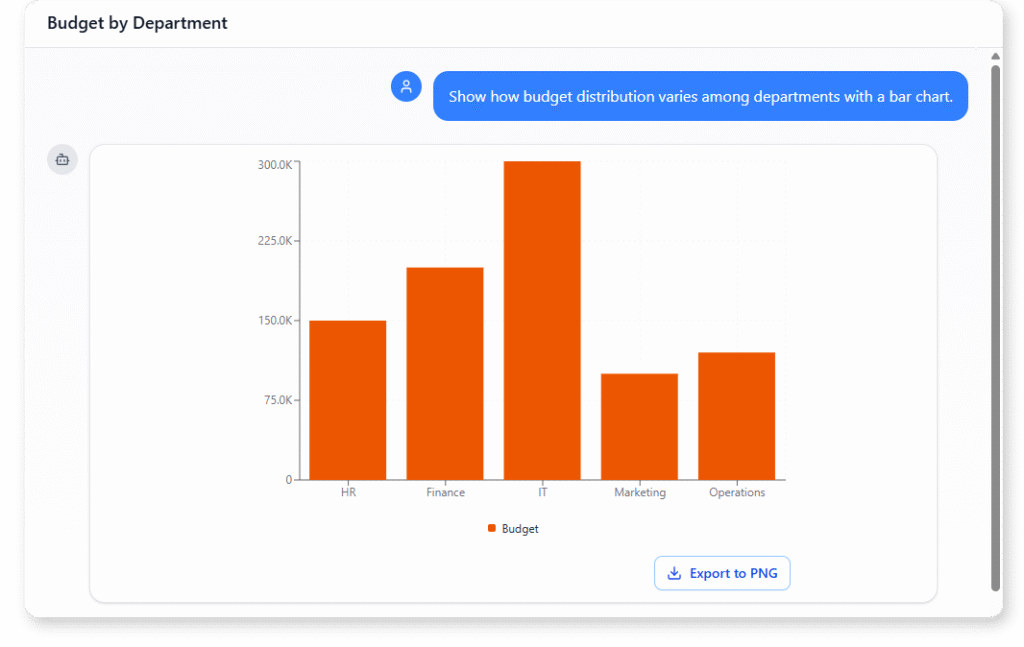
“Show how budget distribution varies among departments with a bar chart. “
Company Price Trends (Line Chart)
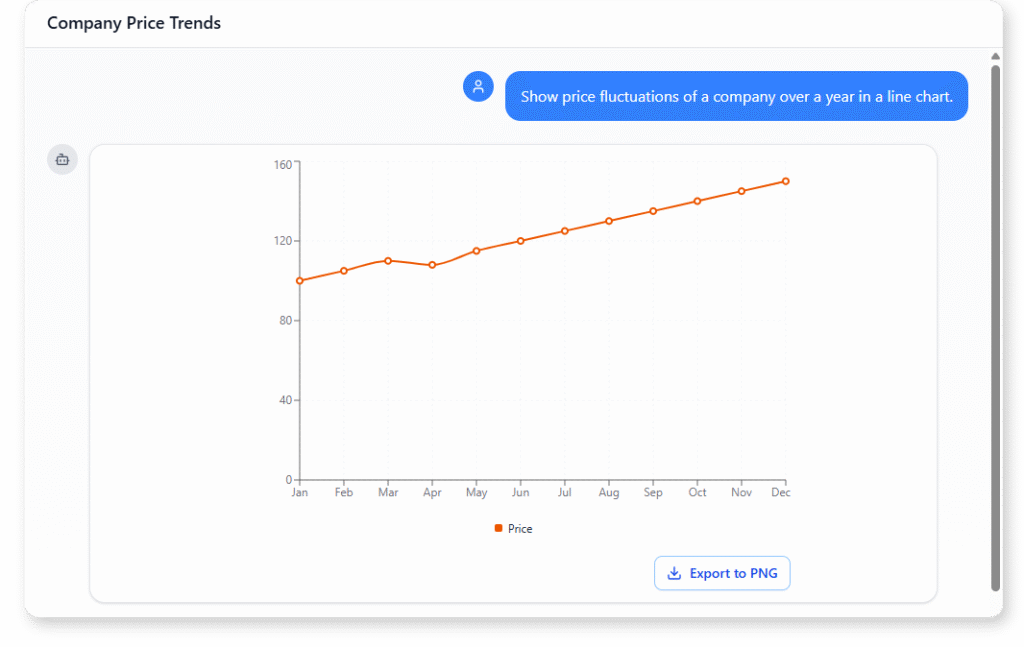
“Show price fluctuations of a company over a year in a line chart.”
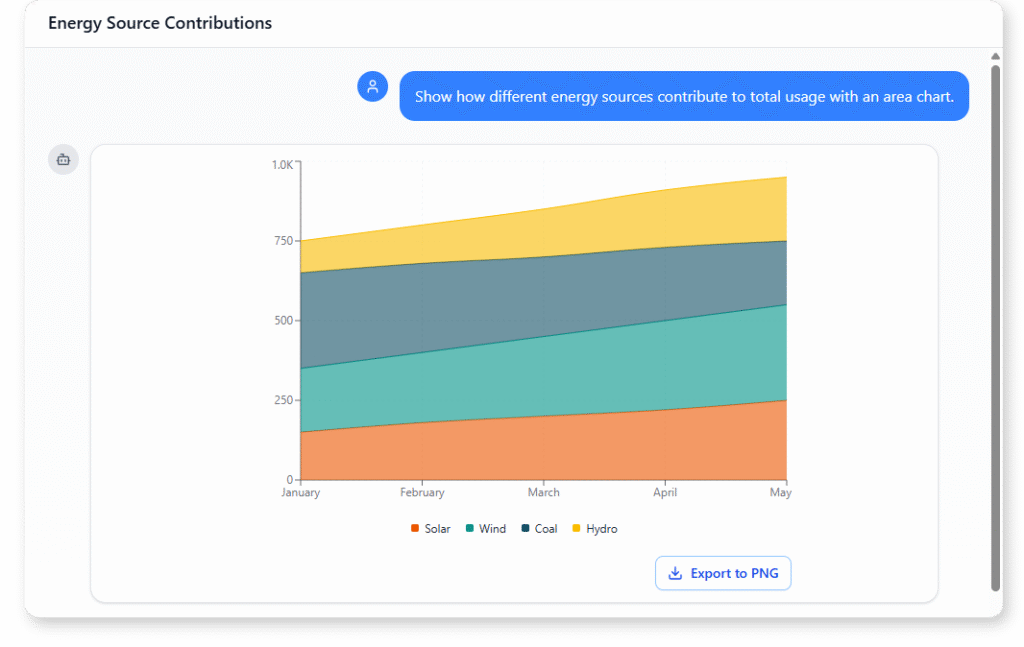
Energy Source Contributions (Area Chart)
“Explore correlation between marketing spend and return with a scatter chart. “
Website Access Visualization (Pie Chart)
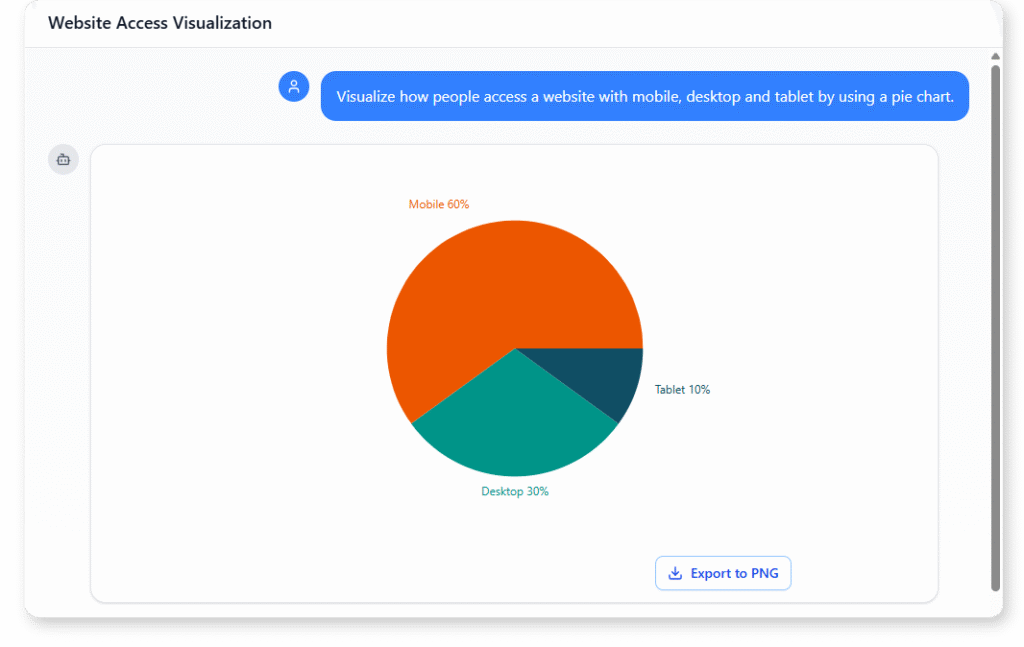
“Visualize how people access a website with mobile, desktop and tablet by using a pie chart.”
Marketing Spend vs Return (Scatter Chart)
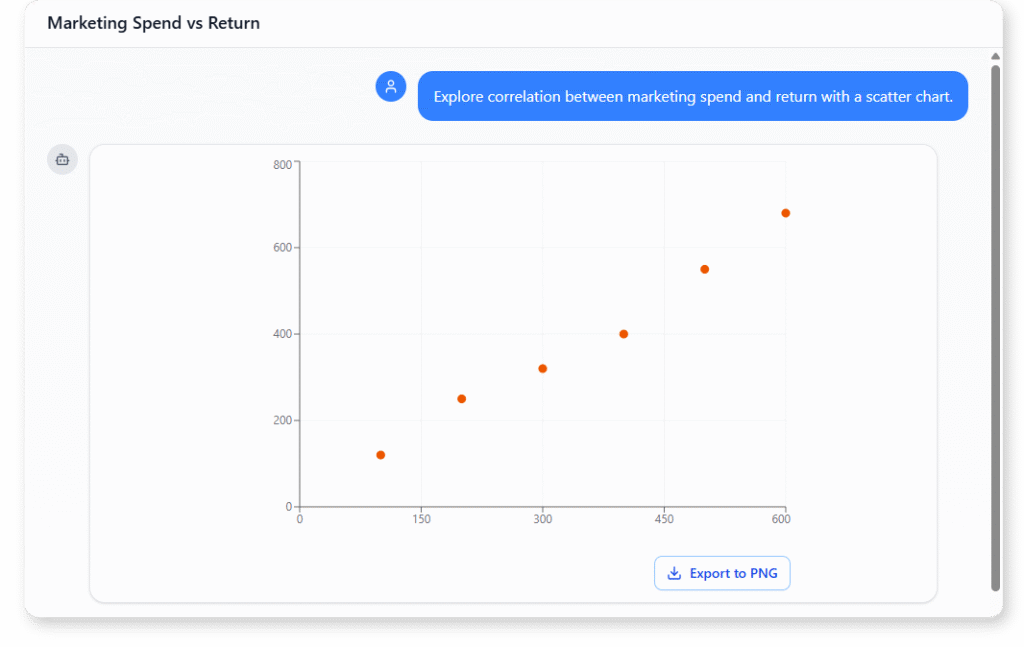
“Explore correlation between marketing spend and return with a scatter chart. “
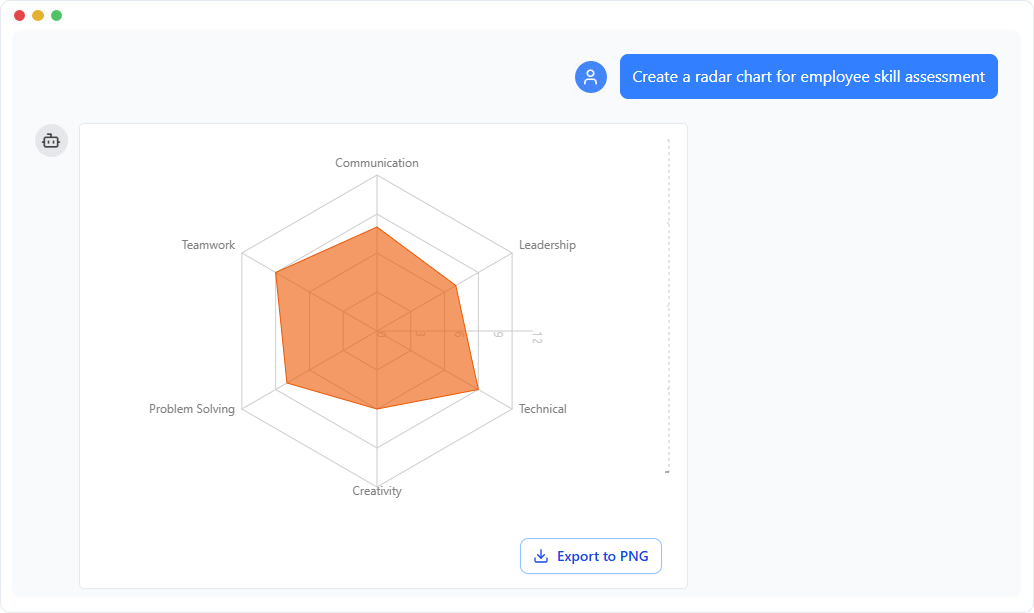
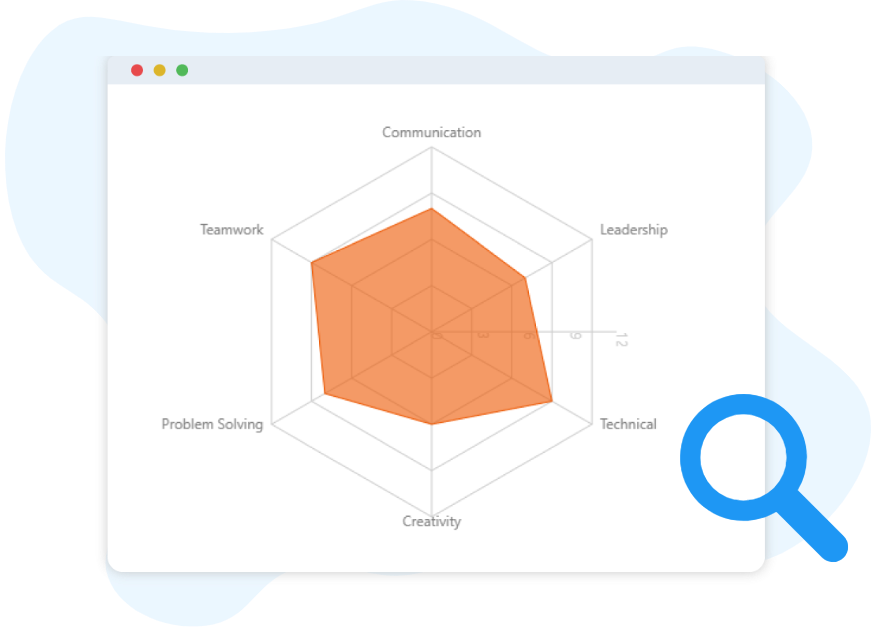
Employee Skills Comparison (Radar Chart)
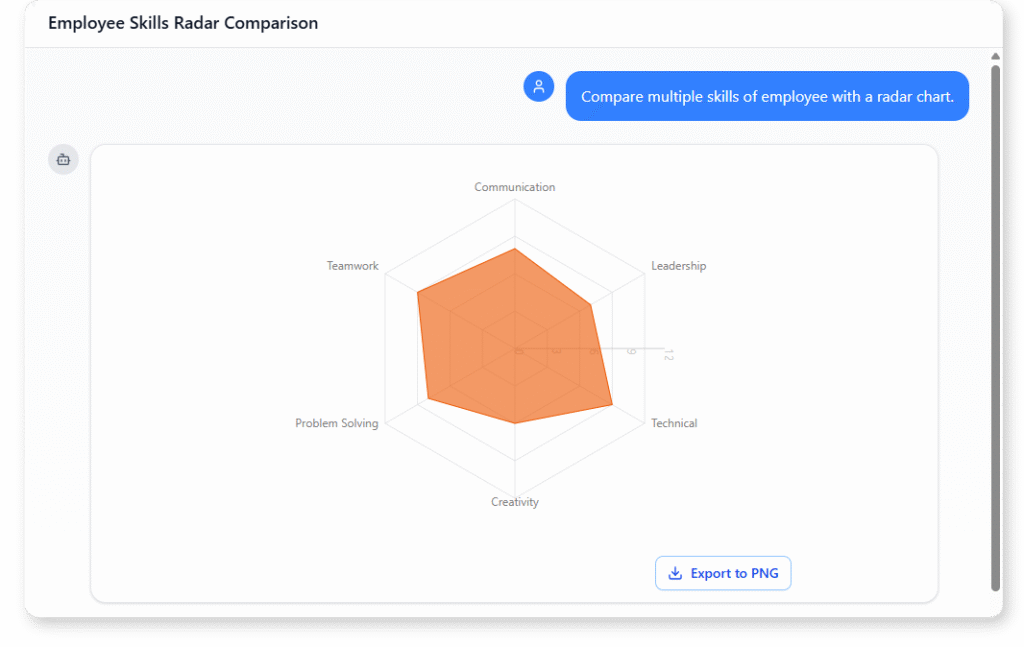
“Compare multiple skills of employee with a radar chart. “
What Is a Chart?
A chart is a visual representation of data, designed to show trends, comparisons, and relationships clearly. Instead of reading through rows of numbers, a chart transforms information into a graphic that is easier to interpret and share. Charts help reveal patterns, highlight differences, and turn complex data into insights at a glance.
There are many kinds of charts—bar charts for comparing values, line charts for trends, pie charts for proportions, scatter plots for relationships, and more. Each chart type offers a unique way to understand your data, making it possible to tell meaningful stories through visual form.
Key Concepts
Chart Types and Their Purpose
Each chart type serves a distinct analytical goal:
Bar Chart – Comparing quantities across categories.
Line Chart – Showing trends and progressions over time.
Area Chart – Demonstrating cumulative or volume-based growth.
Pie Chart – Visualizing parts of a whole.
Scatter Chart – Exploring relationships and correlations between variables.
Radar Chart – Comparing multidimensional performance or attributes.
Understanding these purposes ensures that each visualization aligns with the insight you want to highlight.
Axes and Scales
Axes define how data is measured and compared.
X-Axis (Horizontal): Usually represents categories or time.
Y-Axis (Vertical): Represents values or quantities.
Scales: Can be linear, logarithmic, or percentage-based, depending on data range and purpose.
Understanding axes ensures accurate interpretation of chart proportions and relationships.
Visual Encoding
Charts communicate through visual variables:
Position (e.g., where points are placed on axes)
Length (e.g., height of bars)
Angle (e.g., pie slices)
Color and Shape (e.g., for highlighting or grouping data)
Effective visualization depends on choosing the right encoding method for the message you want to convey.
Data Dimensions
Charts translate data dimensions into visual forms.
Categorical Data: Represents discrete groups (e.g., regions, departments, product types). Commonly visualized using Bar or Pie Charts.
Numerical Data: Represents measurable values, such as sales, cost, or time. Often visualized using Line, Area, or Scatter Charts.
Time-Series Data: Displays data points across time intervals, ideal for tracking trends with Line or Area Charts.
Data Series
A data series is a set of related data points plotted on a chart.
Multiple series allow comparisons (e.g., sales of different products over time).
Series can be color-coded, grouped, or stacked to emphasize contrast or distribution.
Ready to Revolutionize Your Workflow with AI?
Stop wrestling with tools. Embrace AI-powered visual modeling. Let our AI handle the visualization so you can focus on solving the bigger problems.
