In the development of any complex system, from a spacecraft to a medical device, the most critical foundation is a clear, consistent, and traceable set of requirements. The SysML Requirement Diagram is the central tool in Model-Based Systems Engineering (MBSE) for managing this foundation. It provides a visual language to capture requirements, organize them, and link them to the parts of the system that will fulfill them. Managing hundreds or thousands of requirements is a monumental task, but a modern AI assistant can transform this challenge, turning requirements engineering into a dynamic, intelligent, and semi-automated process.
This guide explains the SysML Requirement Diagram and how AI can revolutionize how you manage your system’s requirements.
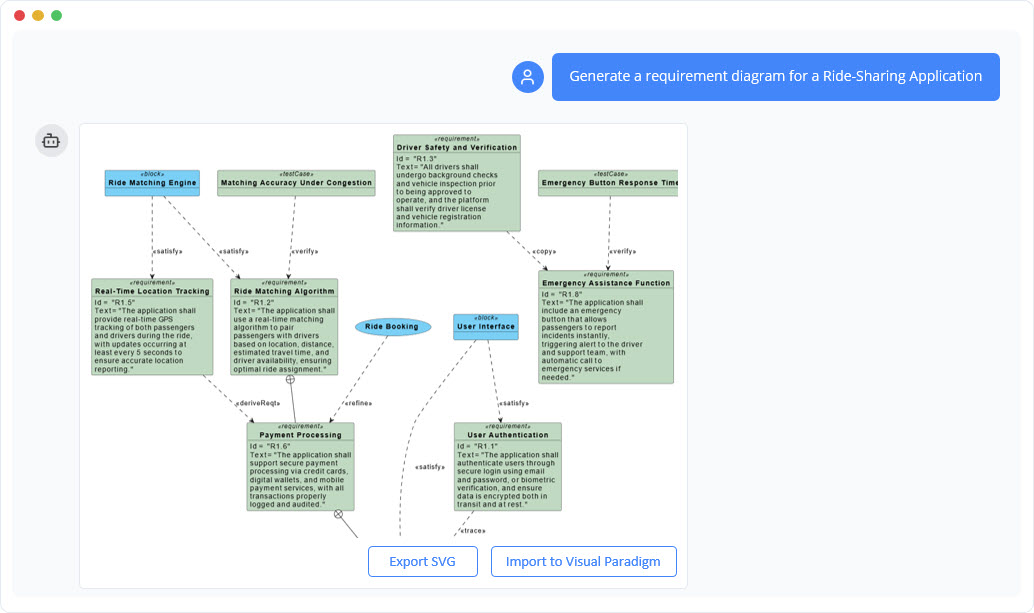
What is a SysML Requirement Diagram?
A Requirement Diagram is used to display system requirements, their relationships to one another, and their relationships to other model elements (like design blocks or test cases).
Core Components
- Requirement: The central element, stereotyped as
<<requirement>>. It contains a unique ID and a text description of a requirement. Requirements can be functional (“The system shall…”) or non-functional (“The system shall be…”). - Package: A folder-like element used to group related requirements into a logical hierarchy.
- Relationships: The diagram’s power comes from visualizing the relationships between requirements and other elements:
- Containment: A simple line showing that a package contains requirements.
<<deriveReqt>>(Derive Requirement): A dependency showing that one requirement is derived from another, more general one.<<satisfy>>: A dependency from a design element (like a Block) to a requirement, showing that the block is intended to satisfy that requirement.<<verify>>: A dependency from a test case to a requirement, showing how the requirement will be verified.<<refine>>: A dependency that adds more detail to a requirement.
Why Use AI for Requirement Diagrams?
Managing a large set of requirements is a major source of project risk. An AI co-pilot acts as a powerful requirements analyst to mitigate this risk.
- From Documents to Models, Instantly: An AI can parse a traditional requirements document (e.g., a Word or Excel file) and automatically generate a structured SysML Requirement Diagram, instantly creating a model from a flat document.
- Intelligent Traceability: Manually creating
<<satisfy>>and<<verify>>links is tedious and error-prone. An AI can analyze the text of requirements and design elements to suggest likely traceability links, dramatically speeding up this critical process. - Powerful Impact Analysis: This is the game-changing capability. Once the traceability model is built, you can ask the AI critical questions: “If we change requirement R-101, what design components and test cases are affected?” The AI can instantly highlight the full impact of a proposed change.
- Automated Quality Checks: An AI can analyze your requirements for common issues. It can flag “orphan” requirements (those with no satisfying element) or identify potentially duplicate or conflicting requirements.
Common Use Cases for Requirement Diagrams
The Requirement Diagram is the backbone of the MBSE process.
- Requirements Elicitation and Organization: Use it in workshops with stakeholders to capture and organize requirements into a logical, hierarchical structure.
- Traceability and Compliance: Create a complete, visual, and auditable trace from high-level stakeholder needs down to detailed design components and their verification tests. This is essential for regulated industries like aerospace and medical devices.
- Change Impact Analysis: Before approving a change request, use the diagram to conduct a rapid and comprehensive analysis of its impact on the rest of the system, enabling informed decisions.
- Guiding System Verification and Validation: The diagram provides a clear map showing which test cases are needed to verify each requirement, ensuring complete test coverage.
How to Generate Requirement Diagrams with AI: Example Prompts
Your prompts should focus on the requirements and their relationships.
- Defining Requirements: “Create a SysML requirement with ID ‘R-01’ and text ‘The vehicle shall accelerate from 0 to 60 mph in under 5 seconds’.”
- Creating Relationships: “Show a
<<deriveReqt>>relationship from requirement ‘R-01’ to a new, more specific requirement ‘R-01.1’.” - Linking to Design: “Create a
<<satisfy>>relationship from the ‘Powertrain’ block to requirement ‘R-01’.” - Impact Analysis: “Based on the model, list all the requirements that are satisfied by the ‘Braking System’ block.”
A Modern Workflow for Requirements Engineering
Embed AI into your requirements process to build a living model.
- AI-Powered Ingestion: Start a project by having the AI ingest existing requirements documents to create a baseline model.
- The Traceability Matrix, Visualized: Use the AI to build and maintain the traceability links. The diagram becomes a living, visual version of a traditional requirements traceability matrix.
- Automated Change Management: Make it standard practice that every change request is first analyzed against the AI-powered model to understand its full impact.
- Continuous Verification: As the project progresses, continuously update the model with
<<verify>>links to test cases, providing a real-time dashboard of requirements coverage.
Conclusion
The SysML Requirement Diagram is the definitive tool for mastering the complexity of system requirements. By pairing its rigorous notation with the analytical power of an AI assistant, we transform requirements engineering from a static, document-based exercise into a dynamic, model-based, and intelligent process. This synergy ensures that we build complex systems that are not only well-designed but are also guaranteed to meet the needs they were intended to solve.


