A UML Activity Diagram is a flow-based visual model that shows how a process progresses from one activity to the next. It highlights decisions, parallel paths, and outcomes, making it ideal for understanding how work moves within a system or organization. Because it focuses on workflow logic rather than technical structure, it is widely used in both business analysis and software design.
Whether you want to explain a user journey, map out an approval process, or refine the behavior of a use case, the Activity Diagram provides a clear view of how tasks connect and how responsibilities shift across different roles or system components. It helps teams improve clarity, reduce ambiguity, and streamline complex processes.
What Is a UML Activity Diagram?
A UML Activity Diagram is a graphical representation of actions and control flows. It illustrates the sequence of steps in a process, including decisions, loops, parallel operations, and final outcomes. Unlike Sequence Diagrams, which focus on message exchange, Activity Diagrams highlight the flow of work.
Teams use them to:
- Document business processes and service workflows
- Clarify system behaviors at the use case level
- Break down complex actions into manageable steps
- Communicate logic to both technical and non-technical stakeholders
The diagram’s simplicity makes it one of the most intuitive UML models for process visualization.
Why Activity Diagrams Are Useful in Real Projects
Activity Diagrams serve many practical purposes across industries and project types:
- Business Process Clarification: They help visualize approvals, handoffs, and dependencies in operations such as onboarding, order handling, or customer support.
- Software Behavior Modeling: Teams can illustrate what happens when a user performs an action, how the system responds, and where alternative paths may occur.
- Identifying Bottlenecks: By seeing the entire process at a glance, you can easily pinpoint inefficiencies or unnecessary steps.
- Improving Communication: Stakeholders understand the workflow without needing technical training, ensuring better alignment during planning.
- Bridging Use Cases and Implementation: They serve as an intermediate model that links functional requirements with technical design.
Key Components of an Activity Diagram
- Action: A single step or operation represented by a rounded rectangle.
- Control Flow: Arrows that show the direction of execution from one action to the next.
- Decision Node: A branching point where the flow diverges based on conditions.
- Merge Node: Converges alternative paths into a single flow.
- Fork Node: Splits the workflow into parallel branches that can run at the same time.
- Join Node: Synchronizes parallel paths before moving to the next step.
- Swimlanes: Organize actions by actor, department, or system component to show responsibility clearly.
These elements help you express simple, linear sequences or complex flows with multiple branches and parallel activities.
Generate UML Activity Diagrams with AI Chatbot
Traditionally, creating Activity Diagrams required manually dragging shapes, placing arrows, and organizing layouts. The AI chatbot removes these barriers by turning plain language into visual diagrams instantly.
You simply describe the flow—such as user actions, system responses, or decision points—and the AI produces a structured Activity Diagram for you. This makes it easy to start modeling even if you are not familiar with UML notation.
Instant Activity Diagram Generation
With the AI-powered diagram generator, you can:
- Describe your workflow in a few sentences
- Let the AI interpret the steps, branches, and sequence
- Receive a complete Activity Diagram in seconds
Example inputs:
- “User logs in, system verifies credentials, user selects an action, and the process ends.”
- “Customer places an order, system checks stock, splits path for payment validation and shipping preparation.”
The AI handles layout, notation, and formatting automatically, helping you focus on the logic instead of the diagram structure.
Refine Workflow Through Conversation
Workflows evolve, and the AI chatbot adapts with you. After the initial diagram is generated, you can refine it naturally:
- Add new steps
- Insert conditions or parallel flows
- Reorder actions
- Introduce swimlanes for different roles
- Remove outdated steps
The diagram updates instantly, allowing you to test ideas, explore alternatives, and perfect the final workflow without redrawing anything manually.
Benefits of Using AI to Create Activity Diagrams
- Ensures correct UML notation for complex structures such as forks and joins
- Produces clean, readable layouts without manual alignment
- Converts plain text descriptions into ready-to-use diagrams
- Allows iterative refinement through simple, conversational adjustments
- Supports swimlane organization for clearer responsibility mapping
- Helps teams maintain up-to-date documentation as processes evolve
The result is faster modeling, clearer communication, and more consistent documentation.
Examples of AI-Generated Activity Diagram Prompts
Here are simple prompts you can use to generate Activity Diagrams immediately:
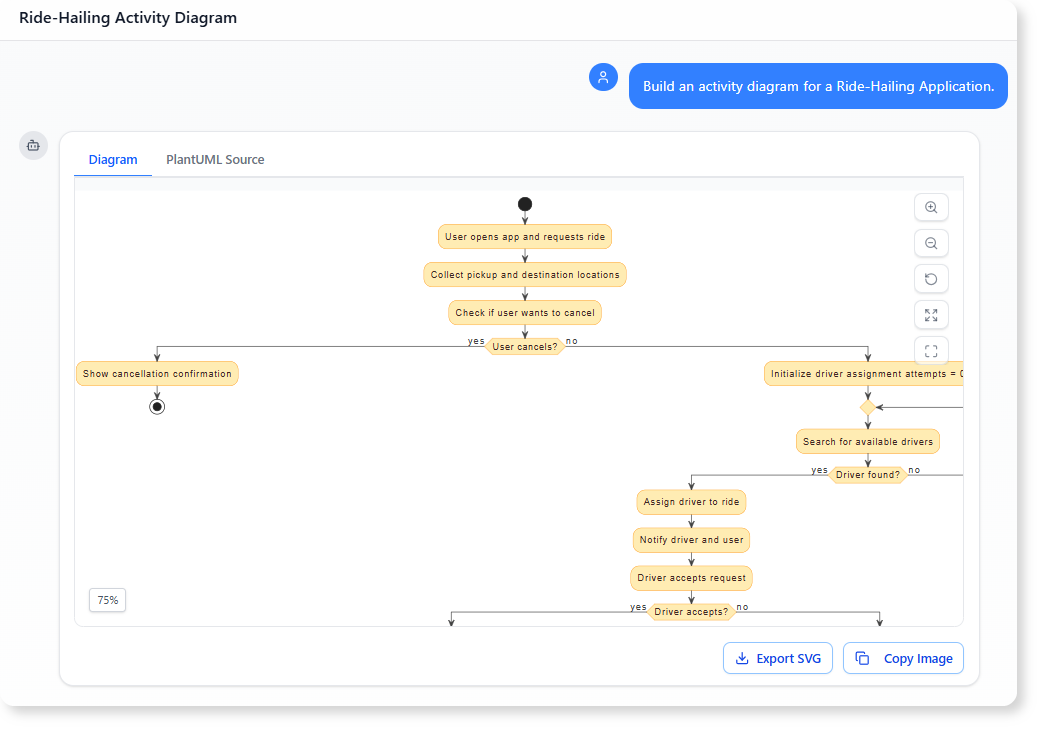
- Ride-Hailing Application: “Build an activity diagram for a Ride-Hailing Application.”
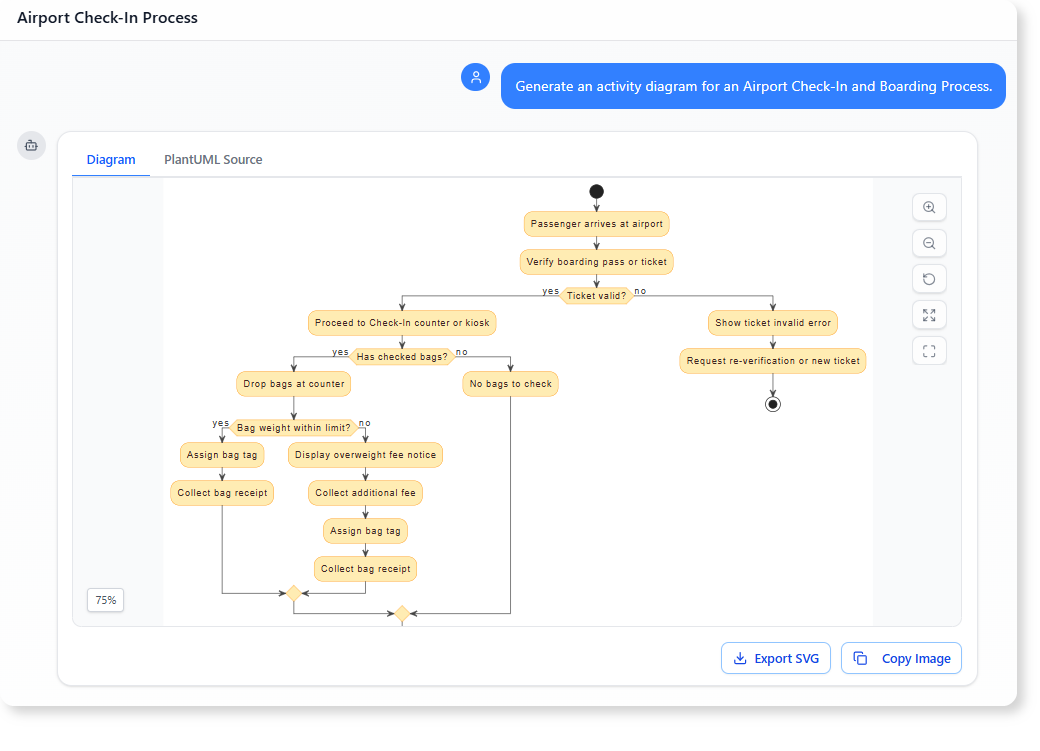
- Airport Check-In and Boarding Process: “Generate an activity diagram for an Airport Check-In and Boarding Process.”
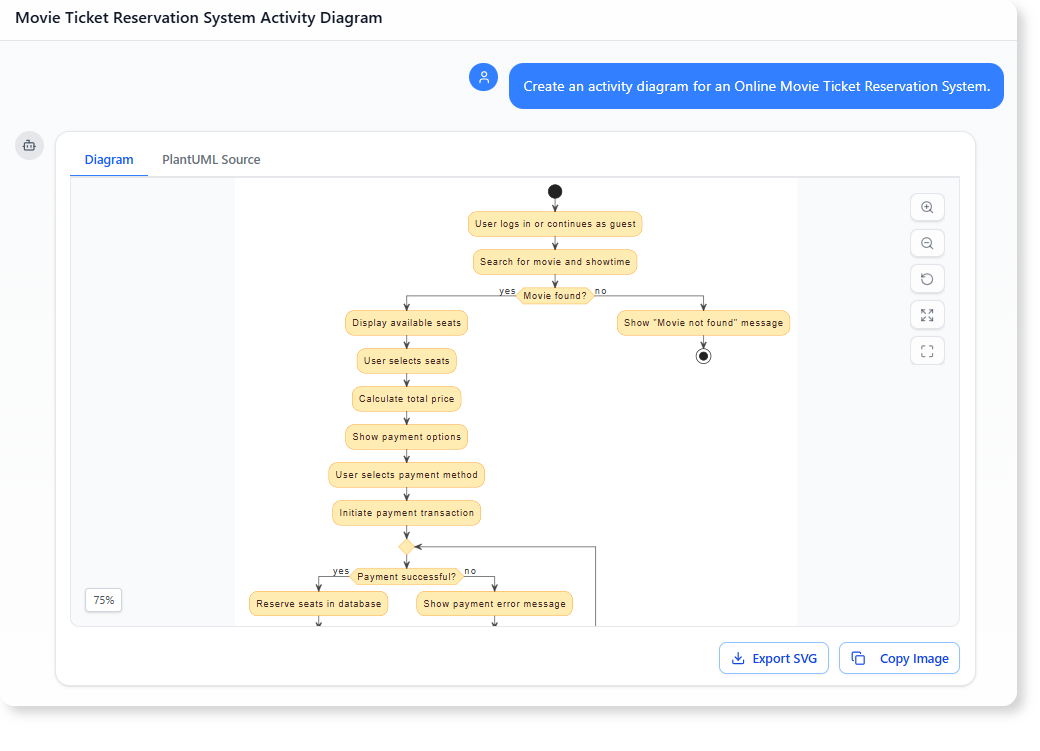
- Online Movie Ticket Reservation System: “Create an activity diagram for an Online Movie Ticket Reservation System.”
These examples can be expanded further with prompts such as:
- “Add swimlanes for user, system, and staff.”
- “Include a parallel branch for security screening.”
- “Insert a decision for payment success or failure.”
When to Use Activity Diagrams in Real Projects
Activity Diagrams are effective in scenarios involving:
- User Journeys: Registration, login, onboarding, and checkout flows.
- Business Workflows: Order fulfillment, claim processing, scheduling, approvals.
- System Behaviors: Background processes, automated tasks, multi-step logic.
- Service Operations: Airport check-in, ticket reservation, transportation routing.
- Coordination Processes: Multi-team collaboration, customer service handling, support escalation.
Any workflow with actions, choices, or parallel steps is a good candidate.
Best Practices for Effective Activity Diagrams
- Keep each action simple and focused on a single task.
- Use swimlanes to clarify responsibility across teams or systems.
- Avoid unnecessary complexity—group related steps or split into multiple diagrams.
- Use decisions wisely for clarity–not every branch needs a complex condition.
- Combine parallel tasks only when they truly occur simultaneously.
- Always verify that the flow leads to a clear, well-defined end state.
These practices ensure readability and maintainability, especially when sharing the diagram with stakeholders.
Final Thoughts: Modernizing Workflow Modeling with AI
Activity Diagrams have long been a valuable tool for visualizing logic and understanding complex workflows. With AI-powered diagram generation, the creation process becomes faster, clearer, and more accessible than ever. You can describe the workflow in everyday language, refine it through conversation, and instantly obtain a structured diagram that follows UML standards.
Whether you are modeling a business process or analyzing a system behavior, AI helps eliminate the manual work—allowing you to focus on designing better, more efficient workflows.


